For years, we evaluated A/B tests in the Universal Analytics (UA) or Google Analytics (GA) or Google Analytics 4 (GA4). When we migrated our data into Snowflake, the ability to query the data became easier (at least for me). The process below saved hours of work within the GA4 interface looking at tests. Only the top portion needs altered based on the test and the report runs the same for all tests.
The Data Scientists and Project Manager team asked me to create a Tableau Dashboard to be able to look at the results of the A/B Tests. Data would need to be broken out by Control and Variant transactions, by Price Buckets, by Booking Window, as well as the ability to see how the lowest price skus were behaving vs all other skus. We needed this part due to price testing. All-in-pricing changed how we approached a lot of decisions in 2025.
As you can tell, it’s a lot of things to account for. But using the Google Analytics Event Table with Experiment IDs that get tracked on the website, as well as 2 other Sales Tables in Snowflake, it could be done. Note that tables and names are all aliased.
-- ===========================================================
-- Example: Session-Anchored A/B Attribution for Purchases
-- Experiment: SR_Show_General (Control vs Variant)
-- NOTE: Replace placeholder schemas/columns to fit your warehouse.
-- ===========================================================
WITH params AS (
SELECT
DATE '2025-10-16' AS start_date, -- demo window start
DATEADD(DAY, -1, CURRENT_DATE) AS end_date_excl_today
),
/* -----------------------------------------------------------
1) ANCHOR EVENTS (per session): page path + matching experiment tag
Take MIN(event_time) per (user, session) where BOTH are true.
- 'page_path' should match your routed page
- 'experiment_groups' is a string/array with assigned variants
------------------------------------------------------------ */
control_anchor AS (
SELECT
e.user_id,
e.session_id,
MIN(e.event_time) AS anchor_ts
FROM analytics.events e
JOIN params p
ON e.event_date BETWEEN p.start_date AND p.end_date_excl_today
WHERE e.page_path ILIKE '%/search/results%'
AND (
-- experiment_groups can be JSON/array/string. Example uses string contains.
(e.experiment_groups || ',') LIKE '%EXP_A%'
)
GROUP BY e.user_id, e.session_id
),
variant_anchor AS (
SELECT
e.user_id,
e.session_id,
MIN(e.event_time) AS anchor_ts
FROM analytics.events e
JOIN params p
ON e.event_date BETWEEN p.start_date AND p.end_date_excl_today
WHERE e.page_path ILIKE '%/search/results%'
AND (
(e.experiment_groups || ',') LIKE '%EXP_B%'
)
GROUP BY e.user_id, e.session_id
),
/* -----------------------------------------------------------
2) PURCHASE TRANSACTION IDS after anchor_ts within SAME session
- Assumes purchase events include a transaction_id
------------------------------------------------------------ */
control_txn AS (
SELECT DISTINCT
e.transaction_id
FROM analytics.events e
JOIN params p
ON e.event_date BETWEEN p.start_date AND p.end_date_excl_today
JOIN control_anchor a
ON a.user_id = e.user_id
AND a.session_id = e.session_id
AND e.event_time >= a.anchor_ts
WHERE e.event_name = 'purchase'
AND e.transaction_id IS NOT NULL
),
variant_txn AS (
SELECT DISTINCT
e.transaction_id
FROM analytics.events e
JOIN params p
ON e.event_date BETWEEN p.start_date AND p.end_date_excl_today
JOIN variant_anchor a
ON a.user_id = e.user_id
AND a.session_id = e.session_id
AND e.event_time >= a.anchor_ts
WHERE e.event_name = 'purchase'
AND e.transaction_id IS NOT NULL
),
/* -----------------------------------------------------------
3) Tag transaction ids by experiment group (for downstream joins)
------------------------------------------------------------ */
experiment_txn AS (
SELECT 'SR_Show_General' AS experiment, 'Control' AS group_type, transaction_id
FROM control_txn
UNION ALL
SELECT 'SR_Show_General' AS experiment, 'Variant' AS group_type, transaction_id
FROM variant_txn
),
/* -----------------------------------------------------------
4) Order Lines at a stable SKU grain
- Replace with your commerce layer tables/joins
------------------------------------------------------------ */
order_lines AS (
SELECT
o.channel,
o.order_id,
o.order_ts::DATE AS order_date,
o.order_reference AS order_reference, -- join key to events.transaction_id
CAST(oi.item_date AS DATE) AS item_date, -- event/item date
oi.product_name,
oi.sku AS item_sku,
SUM(oi.qty) AS item_qty,
SUM(oi.gross_amount) AS item_gross,
SUM(oi.unit_price) AS item_price,
SUM(oi.fee_amount) AS item_fee,
SUM(oi.tax_amount) AS item_tax,
SUM(oi.unit_cost) AS item_cost,
SUM(oi.gross_amount) - SUM(oi.tax_amount) - SUM(oi.unit_cost) AS net_revenue
FROM commerce.orders o
JOIN commerce.order_items oi
ON o.order_id = oi.order_id
WHERE o.order_ts::DATE > DATE '2023-12-31'
AND o.channel = 'WEB'
AND oi.product_type = 'TICKET'
GROUP BY
o.channel, o.order_id, o.order_ts, o.order_reference,
oi.product_name, oi.sku, oi.item_date
),
/* -----------------------------------------------------------
5) Attach experiment group to order lines via transaction id
------------------------------------------------------------ */
base AS (
SELECT
e.experiment,
e.group_type,
ol.channel,
ol.order_id,
ol.order_date,
CAST(ol.order_date AS DATE) AS transaction_date, -- purchase date
ol.item_date, -- event date
ol.order_reference,
ol.product_name,
ol.item_sku,
ol.item_qty,
ol.item_gross,
ol.item_price,
ol.item_fee,
ol.item_tax,
ol.item_cost,
ol.net_revenue
FROM experiment_txn e
JOIN order_lines ol
ON e.transaction_id::STRING = ol.order_reference::STRING
),
/* -----------------------------------------------------------
6) Label time periods (example: YoY comparison)
- Adjust anchors for your narrative
------------------------------------------------------------ */
labeled AS (
SELECT
CASE
WHEN (order_date >= DATE '2024-07-18'
AND order_date < DATEADD(week, -52, CAST(CURRENT_DATE AS DATE)))
THEN 'Last Year'
WHEN (order_date >= DATE '2025-07-17'
AND order_date < CAST(CURRENT_DATE AS DATE))
THEN 'This Year'
END AS period,
experiment,
group_type,
channel,
product_name,
item_sku,
order_id,
transaction_date, -- purchase date
item_date, -- event date
DATEDIFF(day, transaction_date, item_date) AS booking_window_days,
item_qty,
item_gross,
item_price,
item_fee,
item_tax,
item_cost,
net_revenue
FROM base
WHERE
(order_date >= DATE '2024-07-18' AND order_date < DATEADD(week, -52, CAST(CURRENT_DATE AS DATE)))
OR
(order_date >= DATE '2025-07-17' AND order_date < CAST(CURRENT_DATE AS DATE))
),
/* Keep rows with both dates present (charting/BI-friendly) */
labeled_nonnull AS (
SELECT *
FROM labeled
WHERE transaction_date IS NOT NULL
AND item_date IS NOT NULL
),
/* -----------------------------------------------------------
7) Aggregate to daily grain, preserve booking_window
------------------------------------------------------------ */
agg AS (
SELECT
period,
experiment,
group_type,
channel,
product_name,
item_sku,
transaction_date,
item_date,
booking_window_days,
COUNT(DISTINCT order_id) AS num_orders,
SUM(item_price) AS total_item_price,
SUM(item_qty) AS total_item_qty,
SUM(item_gross) AS total_item_gross,
SUM(item_fee) AS total_item_fee,
SUM(item_tax) AS total_item_tax,
SUM(net_revenue) AS total_net_revenue,
SUM(item_cost) AS total_item_cost,
SUM(item_price - item_cost) AS total_margin,
CASE WHEN SUM(item_qty) > 0
THEN SUM(item_price) * 1.0 / SUM(item_qty)
END AS avg_ticket_price
FROM labeled_nonnull
GROUP BY
period, experiment, group_type, channel, product_name, item_sku,
transaction_date, item_date, booking_window_days
),
/* -----------------------------------------------------------
8) Period-level qty-weighted ATP by SKU
------------------------------------------------------------ */
sku_period_avg AS (
SELECT
period,
experiment,
group_type,
channel,
product_name,
item_sku,
CASE WHEN SUM(total_item_qty) > 0
THEN SUM(total_item_price) * 1.0 / SUM(total_item_qty)
END AS period_avg_atp,
SUM(total_item_qty) AS period_qty,
SUM(total_item_price) AS period_price
FROM agg
GROUP BY
period, experiment, group_type, channel, product_name, item_sku
),
/* 9) Rank SKUs by period ATP (lowest = 1) */
sku_period_rank AS (
SELECT
spa.*,
DENSE_RANK() OVER (
PARTITION BY period, experiment, group_type, channel, product_name
ORDER BY period_avg_atp ASC
) AS period_price_rank
FROM sku_period_avg spa
),
/* 10) Attach stable period rank back to daily rows */
ranked AS (
SELECT
a.*,
r.period_avg_atp,
r.period_price_rank
FROM agg a
LEFT JOIN sku_period_rank r
ON r.period = a.period
AND r.experiment = a.experiment
AND r.group_type = a.group_type
AND r.channel = a.channel
AND r.product_name = a.product_name
AND r.item_sku = a.item_sku
)
SELECT
period,
experiment,
group_type,
channel,
product_name,
item_sku,
transaction_date,
item_date,
booking_window_days,
avg_ticket_price, -- daily/txn-grain ATP
period_avg_atp, -- stable ATP over the period
period_price_rank, -- stable rank (1 = lowest ATP)
num_orders,
total_item_price,
total_item_qty,
NULL AS total_order_fees, -- optional placeholder
total_item_gross,
total_item_fee,
total_item_tax,
total_net_revenue,
total_item_cost,
total_margin
FROM ranked;
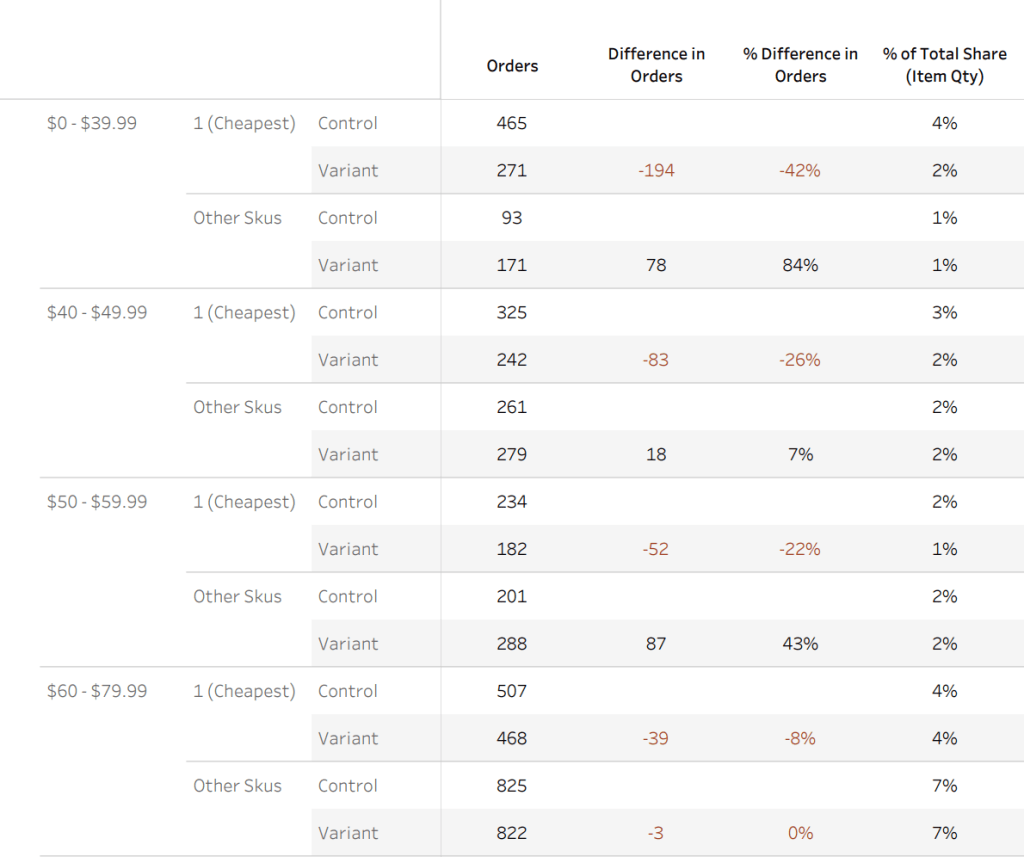
The report goes out in PDF form, but it also can be built with dynamic filters which I use with the data scientists. We can look at any breakdown on the fly.
In one test we found that behavior drastically changed by day of week, this allows us to tweak the test based on day of week to maximize revenue.





Leave a comment